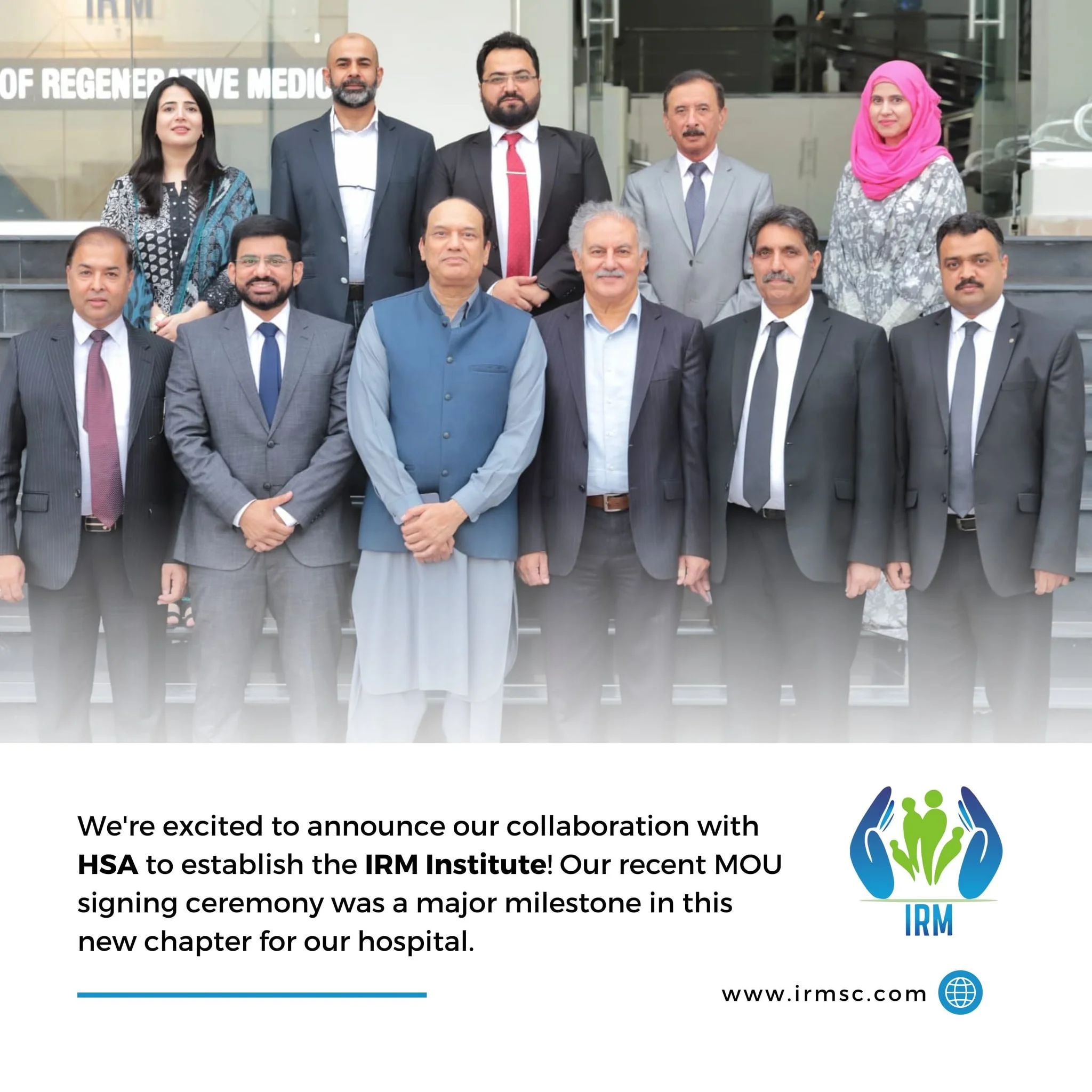
IRM Hospital Islamabad



Emergency Number
Tel: (051) 3757635
Physician Schedule
Service Timing
Finest Patient
Care & Amenities
Stem Cell Therapy
Aesthetics
Physiotherapy
Surgical Treatments
Orthopaedics

Stem Cell Therapy Treatment 24/7
24hrs Emergency Services Open
Our Stem Cell Therapy Treatments are high reliable and authentic.

Best Laboratory Tests Available
All Major Lab Test Services Available
Urgent Lab Test Services for our patients – No delays & Accurate Reports
Stem Cell Therapy Treatment 24/7
24hrs Emergency Services Open
Our Stem Cell Therapy Treatments are high reliable and authentic.
Your Wellness, Our Priority
Our team of healthcare professionals includes experienced physicians, nurses.
Primary Care Excellence
Our experienced primary care physicians take the time to understand your unique health needs.
Emergency Excellence
Rapid Response, Our expert team is trained to respond swiftly to emergencies.
Vascular Surgery
We offer a comprehensive range of services to address vascular issues at every level.
Prescribing Wellness
Our knowledgeable pharmacists are available for personalized consultations.
Surgical Excellence
Our board-certified general surgeons bring a wealth of experience and expertise to perform.
Health Sections
Different Services
Staff Memebers
Satisfied Patients
Transformative Healthcare
at IRM Hospital
Discover a spectrum of specialized care at IRM Hospital, where innovation meets compassion. Our expert teams in Stem Cell Therapy, Physiotherapy, and Pain Management are dedicated to revolutionizing healthcare for a brighter, healthier future.
Stem Cell Therapy 0
Vascular Surgery 0
Gynecological Expertise 0
Physiotherapy 0
Pain Management 0
Aesthetics 0
Our Team
At IRM Hospital, our success is driven by a team of passionate and highly skilled professionals, committed to redefining healthcare. Meet the faces behind our mission:

Dr. Salman Gillani
Stem Cell Expert
Dr. Salman Gillani, a Stem Cell Consultant and Fellow in Stem Cell Therapy is a Diplomat of the American Academy of Anti-aging Medicine and the American Board of Regenerative Medicine.

Maj Gen (R) Professor Dr. Nasim
Orthopedic
Maj Gen (R) Dr. Naseem is a highly qualified orthopedic surgeon with MBBS (PB.), FCPS, and FICS (USA). Specialized in classified surgical procedures, He has advanced training in Orthopedic Surgery from London (UK).

Dr. Shahzad Nasir
Medical Specialist
Dr. Shahzad Nasir is a Medical Specialist and Consultant in Clinical Hematology, serving as a dedicated Bone Marrow Transplant Physician at IRM Hospital in Islamabad. With a focus on hematological care.
Contact us for more information or book an appointment
Read Our Blog
Why Choose IRM Medical Hospital for Your Healthcare Needs?
Why to Choose IRM Hospital for Your Healthcare NeedsSelecting a hospital for your healthcare needs